Describe the Inner Contents of the Nucleus
The outer membrane of a nucleus has many parts. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material DNA of eukaryotic organisms.
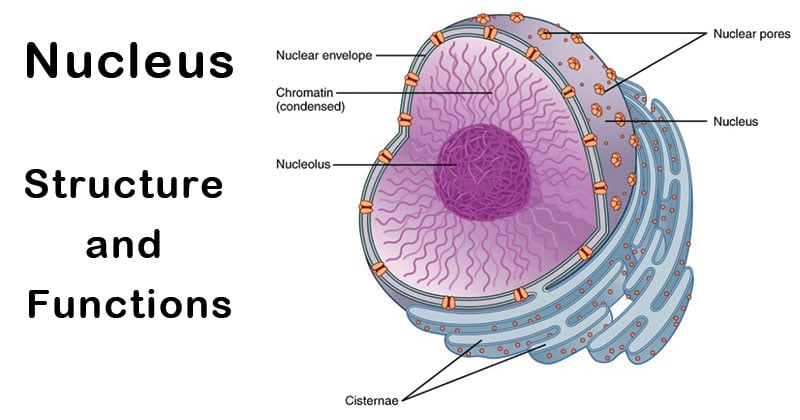
Nucleus Definition Structure Parts Functions Diagram
The Nuclear Envelope - The nuclear envelope is a double-layered membrane that encloses the contents of the nucleus during most of the cells lifecycle.

. Asked By Wiki User. Who is known as suvarna kanya. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a limiting membrane called as.
Some of the eukaryotic organisms have a nucleus that contains up to four nucleoli. Describe the outer membrane of the nucleus. Contained within the nucleus is a dense membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
The nucleus contains a transparent semi-solid granular and homogeneous. As such it serves to maintain the integrity of the cell by facilitating transcription and replication processes. A cell has many jobs such as building proteins converting molecules into energy and removing waste products.
It is also the site of DNA replication formation of an identical copy of DNA. Contains all of the cells DNA except mitochondrial DNA. The mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm via the nuclear pores.
It houses the genome and through translation transcription and post-transcriptional modification it co-ordinates the activities of the cell. Describe the appearance of the nucleolus. The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers the parts of chromosomes carrying the genes for ribosome synthesis.
The Contents of the Nucleus The nucleus is a full house locked and loaded with chromosomes DNA proteins and much more. 5 Main Parts of Nucleus Biology I Nuclear membrane karyotheca. Once an mRNA molecule reaches the cytoplasm ribosomes translate the mRNAs genetic message into the primary structure of a specific polypeptide.
The RNA is manufactured by 5 various sets of chromosomes and kept in the nucleolus. The cytoplasm is composed of two parts the cytosol and organelles. Largest cellular organelle in in eukaryotes.
Cytosol the jelly-like substance within the cell provides the fluid medium necessary for biochemical reactions. The nucleolus appearance is a spot of condensed chromatin. Contained within the nucleus is a dense membrane-less structure composed of RNA and proteins called the nucleolus.
The space between the layers is called the perinuclear space and appears to connect with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The inner nuclear membrane is internally lined by protein filaments meshwork organised in a net-like fashion called nuclear lamina. The nucleus directs protein synthesis by synthesizing messenger RNA mRNA according to instructions provided by the DNA.
It is a membrane bound organelle surrounded by 2 membranes and has a unique well-developed membrane cytoskeleton associated with the inner membrane. The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of the nucleus. The structures are important for the vital functions of the cell nucleus.
The cells chromosomes are also confined within it. The nucleus is a cells central organelle which contains the cells DNA Figure 36. The nucleolus includes RNA and some proteins which resemble those discovered in ribosomes.
Describe the nucleus and its components. In prokaryotes DNA is organized into a single circular chromosome. II Nuclear sap karyolymph or nucleoplasm.
It is engirdled by a structure referred to as the nuclear envelope. These support the nuclear envelope ensuring that the overall shape and structure of the nucleus is maintained. The nuclear envelope separates the fluid inside the nucleus called the nucleoplasm from the rest of the cell.
The proteins that make up the nuclear lamina are known as lamins which are intermediate filament proteins. It contains the genetic information of the cell in the form of deoxyribonucleic acid DNA or chromosomes and thus controls cell growth and multiplication. Later on it is condensed to form the subunits of ribosomes.
The nuclear membrane also called the nuclear envelope is a double membrane layer that separates the contents of the nucleus from the rest of the cellIt is found in both animal and plant cells. Typically it is the most evident organelle in the cell. It is the largest organelle of the eukaryotic cell accounting for around 10 of its volume.
The nucleus contains nearly all of the cells DNA surrounded by a network of fibrous intermediate filaments and enveloped in a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. Describe the contents of a nucleus during interphase. The inner membrane of the nucleus is the membrane which separates the nuclear matrix from the intermembrane space.
The three major functions of the nucleus include. Chromosomes are structures within the nucleus that are made up of DNA the hereditary material. The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle found in the majority of eukaryotic cells.
The nucleus serves several important functions in the cell. The lipid content of the nucleus has been investigated in isolated nuclei. The nucleolus contains nucleolar organizers which are parts of chromosomes with the genes for ribosome synthesis on them.
The nucleoplasm is the semi-solid fluid inside the nucleus where we find the chromatin and the nucleolus. Recently it has been reported that the lipo-protein complex in nuclei from ox spleen and chicken erythrocytes is approximately 10 lipid these give positive tests for phospholipids and cholesterol. In mammals the inner nuclear membrane is associated with heterochromatin and the nuclear lamina.
To understand chromatin it is helpful to first consider chromosomes. Nucleoplasm Nuclear Sap 4. The nuclear envelope is made up of two concentric membranes each of 7-8 nm thickness.
The nuclear membrane forms an envelope like structure around the nuclear contents and is commonly known as a nuclear envelope. Nuclear Membrane Definition. The envelope is perforated with tiny holes called nuclear pores.
The nucleus is composed of various structures namely nuclear envelope nucleoplasm or nucleus sap nuclear matrix chromatin and nucleolus. The following points highlight the six main components of the nucleus found in cells. Describe the inner contents of the nucleus.
Its the largest organelle inside the cell taking up. Nucleolus is a little round granular structure of the nucleus Each nucleus includes several nucleoli. The nuclear envelope separates the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm.
Nucleolus RNA DNA. The nucleus is completely bound by membranes. The inner conents are thick ropy strands called chromatin and the large solid spot is the nucleous.
Describe the inner contents of the nucleus.
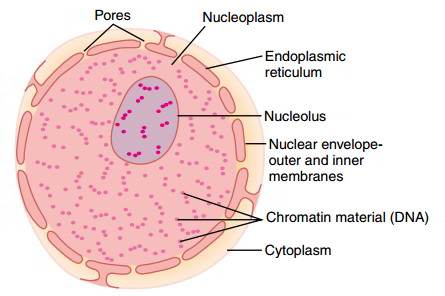
Nucleus Structure Components And Functions Earth S Lab

Comments
Post a Comment